
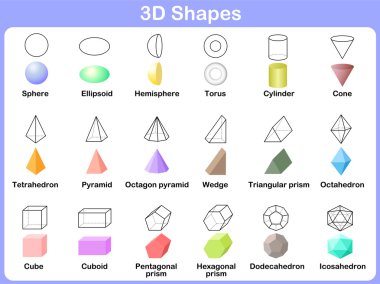
The opposite faces on a cuboid are equal in size.Ī cuboid has 12 edges. A cuboid is also known as a rectangular prism.Ī cuboid has 6 rectangular faces. It is an elongated cube.Ī cuboid is a 3D box shape and it has rectangular faces. There are 4 vertices on the top square face and 4 vertices on the bottom square face.Ī cuboid has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices. There are also 4 vertical edges connecting the top square face to the bottom square face. There are 4 horizontal edges around both of the top and bottom square faces. There are 12 edges on a cube, which are all the same length. All of its edges are the same length.Įach of the 6 faces of a cube is square-shaped because all of its edges are the same size. Marking the faces, edges and vertices as you count them is important as it can be easy to count them twice or miss one out.Ī cube has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices. You could put a sticker or piece of plasticine on each vertex as you count it. You can mark each edge as you count it by drawing a line on each one. You can colour in each face a different colour, or write a number from 1 – 6 on each square face. When teaching this topic, it can be helpful to count the number of each property on the net before assembling it. Alternatively, there are some online interactive 3D shapes in the practice section above that you can use to count the faces, edges and vertices. There are also printable nets for each 3D shape above that can be downloaded and assembled to accompany this lesson. When teaching the properties of 3D shapes, it is worth having a physical item to look at as you identify and count each property. All three dimensional shapes have the the three dimensions of length, width and depth.Ī shape is 3D if it can be picked up and held in real-life. The following table lists the number of faces, edges and vertices for some common 3D shapes:ģD is short for three-dimensional. The poster below shows the faces, edges and vertices of 3D shapes labelled on a cube.

Vertices are the corners of a 3D shape formed where two or more edges meet.įor example, a cube has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices.Edges are the lines where two faces on a 3D shape meet.Faces are the flat or curved surfaces that make up the outside of a 3D shape.

Good Luck.The properties of 3D shapes are faces, edges and vertices. Use the comment section below and provide your views. I hope the article was useful when differentiating between the two shapes. Basically, 2D shapes can be produced on a flat surface and they tend to have two-axis while 3D shapes have three axes. The core differences between 2D and 3D shapes are quite clear according to the discussion above. Besides that, there is a necessity of high configuration technologies for 3D Animation but for 2D Animation normal computer is enough. Hence making it complex since you have to capture the 3D motion.ĢD Animation is less expensive and takes less time to learn in comparison to 3D animation, which is very expensive. But it occupies the three- dimensional volume behind an object with light in front of it.ģD animation will take much much longer than 2D. The cross-section of a shadow is a two– dimensional silhouette.
All creatures such as ants have 2D shapes hence lack a sense of depth.3D have hidden edges while 2D shapes have edges that are visible.2D shapes have two dimensions while the 3D shapes have three dimensions.Main Differences Between 2D and 3D Shapes 3D design is also crucial in 3D printing. The dimension is quite ideal in all engineering drawings.Įxamples of shapes with 3D are cube, cuboid, pyramid, and spheres among many others. Some of the common shapes that have 3D are buildings, boxes, and furniture. The type of dimension is used in animation, building designs, Bridge designs, and drawing graphs. What Are 3D Shapes?ģD shapes are solid objects that have length, width, and height. Geological maps are an example of 2D shapes since they use the contouring method to show the depth with the assistance of shapes.īesides that, all parallel projections and one-point perspective projection plans are other examples that rely on 2D.Īll the drawings made on the floor, walls, tiles, and fabrics are some of the applications of 2D in real life. According to research, a 2D shape can be produced on a flat surface. 2D shapes are those that contain both the length and the width.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
